퍼즐(Gold 2)
문제
1525번: 퍼즐
세 줄에 걸쳐서 표에 채워져 있는 아홉 개의 수가 주어진다. 한 줄에 세 개의 수가 주어지며, 빈 칸은 0으로 나타낸다.
www.acmicpc.net
접근법
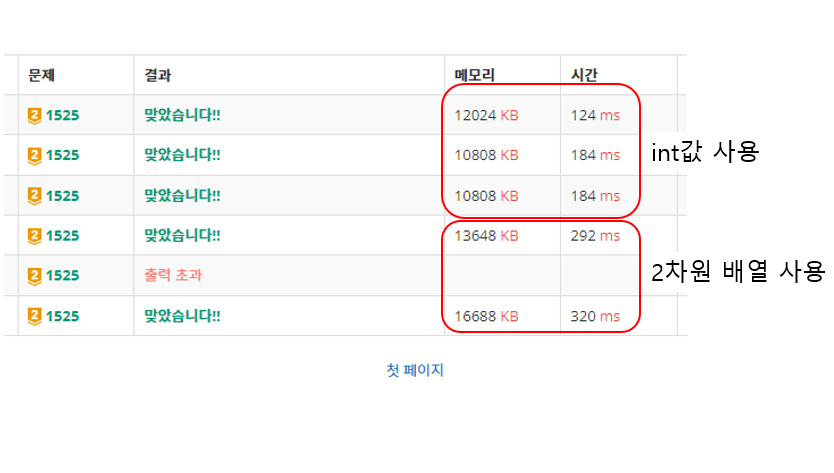
퍼즐이 한 칸씩 움직이는 경우에 대해서 너비 우선 탐색을 진행하여 최소 거리를 구할 수 있는 문제입니다. 퍼즐의 모양을 저장하기 위해서 2차원 배열을 사용할 수 있지만 1~9까지 수를 9개 저장하고 비교하기 위해서 배열을 사용하는 것은 공간과 시간에 낭비가 발생합니다. 반면 000,000,000 ~ 999,999,999까지 사용할 수 있는 4바이트 int 타입 하나로 퍼즐을 나타내고 값을 비교한다면 9개의 정수 배열을 활용하는 것에 비해 사용하는 공간과 시간을 많이 절약할 수 있습니다.
3*3 퍼즐을 다음과 같이 표현할 수 있습니다.
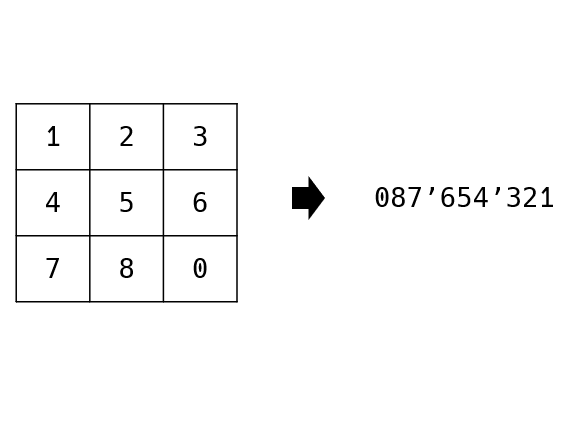
3*3 퍼즐을 int 값으로 변환하는 방법은 다음과 같습니다.
int MapToInt(const Map& map)
{
int fac = 1;
int retval{};
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; ++j)
{
retval += map[i][j] * fac;
fac *= 10;
}
}
return retval;
}이제 이 int 값으로 BFS 탐색을 실행할 수 있습니다. BFS 탐색 코드는 아래에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
전체 코드
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <array>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
struct Pos {
Pos() {}
Pos(int _r, int _c) : r{ _r }, c{ _c }{}
int r{};
int c{};
Pos& operator+= (const Pos& other)
{
r += other.r;
c += other.c;
return *this;
}
};
Pos operator+(const Pos& lhs, const Pos& rhs)
{
return Pos(lhs.r + rhs.r, lhs.c + rhs.c);
}
using Map = array<array<int, 3>, 3>;
struct Move {
int dep{};
Pos zero{};
int i_map;
};
Map puz;
unordered_set<int> vis;
const array<Pos, 4> dir{ Pos(1,0),Pos(-1,0),Pos(0,1),Pos(0,-1) };
int MapToInt(const Map& map)
{
int fac = 1;
int retval{};
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; ++j)
{
retval += map[i][j] * fac;
fac *= 10;
}
}
return retval;
}
bool IsOut(const Pos& pos)
{
if (0 <= pos.c && pos.c < 3 && 0 <= pos.r && pos.r < 3)
return false;
else
return true;
}
void Shift(int& i_map, Pos& cur, const Pos& dir)
{
Pos next = cur + dir;
int curIdx = cur.c + cur.r * 3;
int nextIdx = next.c + next.r * 3;
int nextFac = pow(10, nextIdx);
int nextVal = i_map / nextFac;
nextVal -= ((int)(nextVal / 10)) * 10;
int curFac = pow(10, curIdx);
// 0위치에 nextval 삽입
i_map += nextVal * curFac;
// nextval 위치를 0으로 설정
i_map -= nextVal * nextFac;
// zero 위치 이동
cur += dir;
}
void printMap(int i_map)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; ++j)
{
cout << i_map % 10 << " ";
i_map /= 10;
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
int BFS()
{
Map target_Map;
target_Map[0] = { 1,2,3 };
target_Map[1] = { 4,5,6 };
target_Map[2] = { 7,8,0 };
int i_target = MapToInt(target_Map);
Move start;
start.i_map = MapToInt(puz);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < 3; ++j)
if (puz[i][j] == 0)
{
start.zero.r = i;
start.zero.c = j;
break;
}
start.dep = 0;
if (start.i_map == i_target) return 0;
queue<Move> q;
vis.insert(start.i_map);
q.push(start);
while(!q.empty())
{
Move cur = q.front();
q.pop();
//printMap(cur.i_map);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
if (IsOut(cur.zero + dir[i])) continue;
Move next = cur;
Shift(next.i_map, next.zero, dir[i]);
next.dep += 1;
if (vis.find(next.i_map) != vis.end()) continue;
vis.insert(next.i_map);
if (next.i_map == i_target) return next.dep;
q.push(next);
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
//입출력 성능향상을 위한 설정
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cout.tie(NULL);
cin.tie(NULL);
for (auto& row : puz)
{
for (int& n : row)
{
cin >> n;
}
}
int answer = BFS();
cout << answer << endl;
return 0;
}